Morchella, commonly known as the true morels, are a unique genus of edible mushrooms known for their distinct honeycomb appearance. Highly valued in culinary circles, especially in French and Catalan cuisine, these morels belong to the Ascomycota fungi division, closely related to the simpler cup fungi in the order Pezizales. Morels are not just sought after for their taste, but also for their rarity, as they are notoriously challenging to cultivate commercially.
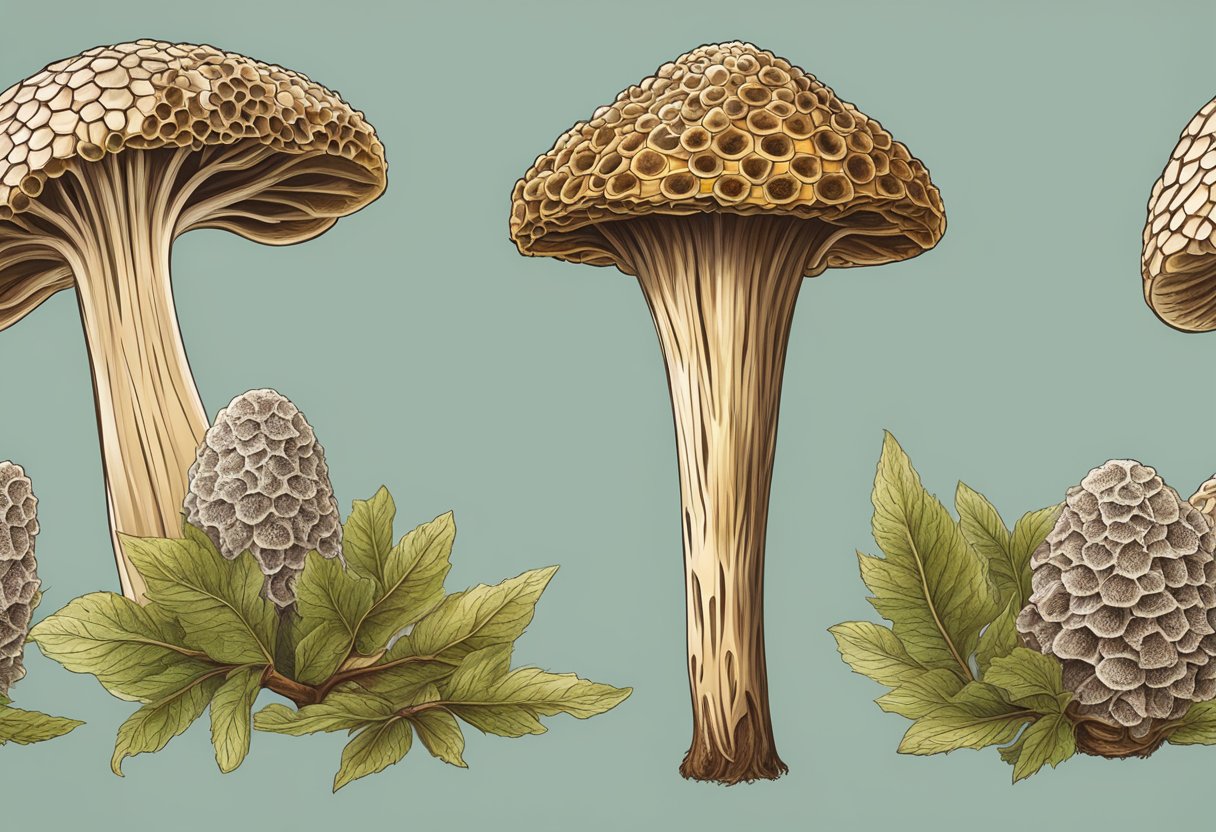

To identify Morchella mushrooms, one would look for their characteristic ridged and pitted caps, which give the mushrooms their honeycomb-like structure. Different species within the Morchella genus vary in color and size, such as the Morchella esculenta (common morel), Morchella elata (black morel), and the less commonly known Morchella diminutiva (yellow morel). Knowing where and when morel mushrooms grow is key, as these critical factors for their survival play an essential role in their distribution and habitats.
Key Takeaways
- Morchella, or true morels, are a distinct and rare genus of edible mushrooms prized for their unique honeycomb appearance and culinary value.
- Knowing how to identify Morchella mushrooms is crucial, as species differ in color and size, and require specific habitats for healthy growth.
- Although difficult to cultivate commercially, the increasing appreciation for their taste in gourmet cooking has fueled interest in understanding and responsibly harvesting these delightful fungi.
Description and Identification of Morchella
Morchella, commonly known as morel mushrooms, are a highly prized and sought-after species of fungus. They belong to the Morchellaceae family and are known for their distinct appearance, which sets them apart from other mushrooms.
Coloring and Texture
True morels have a unique, spongy cap with a combination of ridges and pits. The color of the cap can range from a lighter tan to dark brown shades, depending on the species. The ridges are typically pale or cream-colored, while the pits are darker. The flesh of the morel is white, firm, and brittle.
The cap of the Morchella can be oval or elongate in shape. Its texture significantly contributes to the overall identification of this mushroom. The cap is attached to a thick, white, stout stem, which adds to its distinct appearance.
When searching for the largest morel mushrooms, one must be cautious, as their unique shape and size can vary across species. Morels grow in various habitats, but they’re commonly found in woodland areas, especially near dead or dying trees.
To safely identify and consume morel mushrooms, it’s essential to understand their physical characteristics and know how to differentiate them from toxic or inedible lookalikes.
In summary, the key features to recognize Morchella include their distinct cap with its ridges and pits, the combination of tan and cream colors, and the elongate or oval shape of the cap. Proper knowledge and identification techniques can significantly contribute to a successful foraging experience, allowing enthusiasts to enjoy this highly sought-after and flavorful species of mushrooms.
Habitat and Distribution
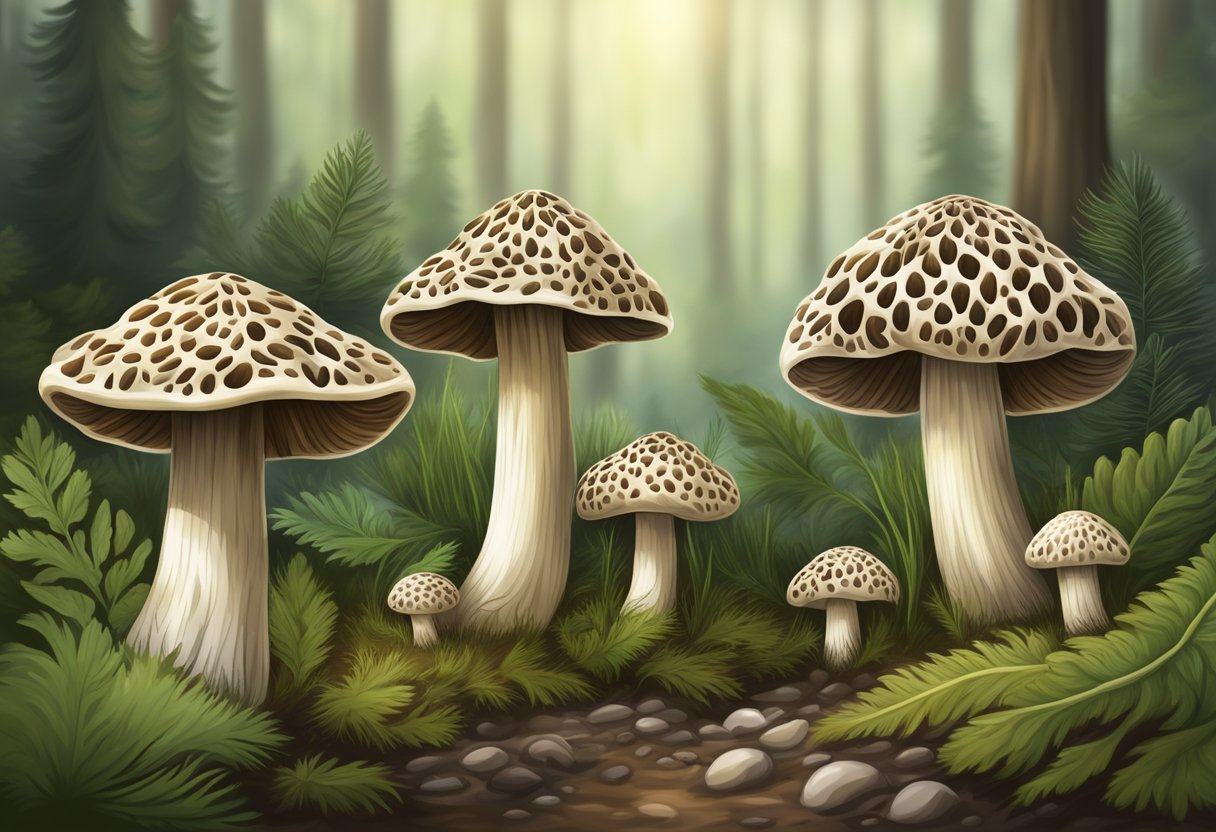

Morchella, also known as morel mushrooms, have a widespread distribution and can be found in various habitats across the globe. Their preference for specific environmental conditions and growth substrates can differ based on the region they are found in.
North American Morchella
In North America, Morchella species are commonly found in hardwood forests, particularly around trees such as elm, ash, and apple. They often grow in soils rich in organic matter, and the presence of dead or decaying wood may increase their likelihood of occurrence. Morels can also be found in areas with recent disturbances such as wildfires or in ash-laden soils. Some regions in Western North America, like Oregon and Idaho, are known for their abundant morel growth in conifer forests, especially after forest fires.
European Morchella
In Europe, the distribution of Morchella species varies throughout the continent. France, Germany, and Turkey are some of the countries known for their morel populations. European morels commonly grow in association with hardwoods, such as elm and apple trees, as well as in areas with shade and well-draining soils. While Morchella species can be found in both coniferous and deciduous forests, they show a preference for hardwood-dominated areas. Similar to their North American counterparts, European Morchella can also be found in disturbed habitats such as forest fire sites or areas with decaying wood.
In both North America and Europe, Morchella species have specific growing seasons that vary based on local climate and weather conditions. Foragers should be aware of these seasonal patterns to increase their chances of finding these elusive and highly sought-after mushrooms.
Types of Morchella
Black Morel
Black morels are a group of Morchella species characterized by their dark color and distinct honeycomb-shaped, ridged caps. Common species within this group include Morchella angusticeps, Morchella conica, and Morchella elata1. These mushrooms are highly sought after by foragers for their unique appearance and delicious flavor. They typically grow in forests and can be found in various regions around the world.
Yellow Morel
Yellow morels, also known as grey morel mushrooms, are another type of Morchella that sports a lighter coloration. They have a conical cap and a honeycomb-like structure similar to other morels2. Common species of yellow morels include Morchella deliciosa and Morchella esculenta1. These mushrooms are valued by chefs and foragers alike for their unique appearance, meaty texture, and nutty flavor.
Common Morel
The common morel, Morchella esculenta, is a popular edible mushroom known for its unique appearance and tasty culinary properties. It is sometimes considered a type of yellow morel due to its similar appearance and coloration3. Common morels have a honeycomb-like cap with a conical shape and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests and grassy areas. They are a favorite of foragers and mushroom enthusiasts, making them a popular choice in many wild mushroom dishes.
Footnotes
Morchella Lifecycle
Spore Germination
Morchella, also known as morel mushrooms, begin their lifecycle with the germination of spores. These spores are a crucial component for the growth and development of morel mushrooms, known for their unique taste and distinct appearance. Upon finding suitable environmental conditions, the spores germinate and give rise to mycelium.
Mycelium Formation
Once spores germinate, the mycelium forms, a network of fungal filaments that extend and branch out within the soil. During this stage, the mycelium remains hidden from view and grows a few inches deep underground. The mycelium structure plays a vital role in nutrient uptake and eventually leads to the development of fruiting bodies.
Fruiting Body Development
The development of fruiting bodies marks the final stage in the Morchella lifecycle. These fruit bodies are the visible, above-ground portion of the mushroom that we often recognize as morels. They are characterized by their unique honeycomb-like appearance and hollow structures. This stage is crucial for the reproduction process, as the fruiting bodies contain asci filled with spores, which are essential for the propagation of morels.
Fruiting body development takes place under specific environmental conditions that are conducive for morel mushrooms growth. Once mature, the fruiting bodies release their spores back into the environment, allowing for the germination process to begin anew and continue the Morchella lifecycle.
Culinary Uses of Morchella
Morchella, also known as morel mushrooms, are a highly sought-after wild fungi prized for their unique flavor and meaty texture. In this section, we will discuss harvesting, cooking, and the enjoyment of these edible mushrooms.
Harvesting
Finding and harvesting morel mushrooms can be an exciting endeavor, as these fungi are known for growing in specific conditions and being somewhat elusive. Many foragers rely on experience and knowledge of the local environment, as morels can be found in areas with moist soil, near trees such as elm, ash, and sycamore. As with any wild-foraged food, be cautious and sure of your identification before consuming.
When you do locate morel mushrooms, sustainable harvesting is essential. It’s crucial to use a gentle approach, collecting morels carefully to avoid damaging the fungi or the surrounding ecosystem. It’s also recommended to store them properly to maintain their delicate flavor and texture before cooking.
Cooking
The unique taste and texture of morels make them highly desirable in a variety of dishes. Described as rich and nutty, the flavor profile is often appreciated even by those who don’t typically enjoy other mushroom varieties.
To prepare fresh morel mushrooms, start by cleaning them thoroughly to remove any dirt, insects, and debris. Some chefs recommend soaking the morels in saltwater or dampening them slightly to ensure they’re clean. Once clean, the morels can be cooked in a number of ways, such as pan-frying, grilling, or incorporating them into complex dishes.
With their rich flavor and meaty texture, morels often make excellent additions to sauces, risottos, pasta dishes, and even the centerpiece of an elegant entrée. Fresh morel mushrooms can also be prepared as a simple, yet delicious, side dish to complement your main course.
Due to their popularity and the challenges in cultivating them, morel mushrooms can be quite expensive. Their price reflects the high demand and limited supply, making them a coveted ingredient among chefs and food enthusiasts alike.
In conclusion, Morchella mushrooms bring an exquisite taste and delightful texture to the culinary world, making them a cherished delicacy for those fortunate enough to find and enjoy them.
The Science Behind Morchella

Morchella, commonly known as morel mushrooms, are a genus of fungi considered a culinary delicacy in various cuisines. They possess a distinctive honeycomb appearance and are closely related to the cup fungi in the Pezizales order. This section delves into the scientific aspects of Morchella, exploring the evolutionary history and genetic analysis of this fascinating genus.
Evolutionary History
The genus Morchella has a rich evolutionary history, with numerous species found across the globe. Thanks to molecular phylogenetics and DNA analysis, researchers have been able to better understand the phylogeny and classification of these mushroom species. The study of Morchella’s evolutionary history is crucial in shedding light on their ecological roles, physiological characteristics, and potential applications in various industries, such as food and medicine.
Genetic Analysis
In recent years, the genetic analysis of Morchella species has gained importance. One notable method employed by scientists is multilocus molecular analysis to study and identify Morchella samples. In addition, whole-genome sequencing has been carried out on certain Morchella species, such as M. sextelata, providing invaluable genomic data for further investigation. The genetic analysis of Morchella plays a vital role in enhancing the understanding of their biology and improving cultivation techniques. Moreover, it might help to decipher the properties that make these fungi so highly prized, beyond their unique appearance and culinary appeal.
Through the study of Morchella’s evolutionary history and genetic analysis, researchers aim to not only understand their scientific background but also to promote their conservation and sustainable use. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring that future generations can also appreciate the gastronomic delicacy and potential applications of this remarkable fungus.
References
In the study of Morchella, also known as true morels, researchers have conducted extensive research on various aspects such as taxonomy, species diversity, distribution, ecological factors, and cultivation techniques. The unique honeycomb appearance of morels makes them a prized delicacy, particularly in French and Catalan cuisine, appreciated by gourmet cooks around the world1.
Extensive research has led to significant advances in understanding Morchella taxonomy, species diversity, and distribution. Scientists use DNA barcoding techniques to identify and classify Morchella species, providing a reliable way to distinguish between different species and determine their geographic distribution2.
Studies have also investigated morels’ ecological diversity, focusing on their dependence on specific habitat conditions3. Morel mushrooms have a symbiotic relationship with certain tree species, which is crucial for their growth and development. Various factors, including soil composition and moisture levels, influence the occurrence and abundance of morels in different regions.
Artificial cultivation of morel mushrooms has gained increasing interest due to their economic and cultural significance4. Recent research works have shed light on the genomic information of Morchella sextelata, contributing to the development of improved culturing techniques5.
Moreover, investigations regarding soil microbial diversity and evenness have been conducted to understand their impact on morel production6. This line of research helps to optimize cultivation practices, making large-scale farming of morels more feasible and sustainable.
Footnotes
- Morchella – Wikipedia ↩
- DNA Barcoding and Species Classification of Morchella ↩
- A review on research advances, issues, and perspectives of morels ↩
- Artificial cultivation of morels ↩
- The whole-genome sequence analysis of Morchella sextelata ↩
- Morel Production Related to Soil Microbial Diversity and Evenness ↩
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the common name for Morchella?
Morchella mushrooms are commonly known as morel mushrooms. They are a highly prized edible fungus, known for their distinctive appearance and unique flavor.
Why are Morchella so expensive?
Morel mushrooms are expensive due to their rarity and difficulty to cultivate. They predominantly grow in the wild and are typically found in forested regions. Harvesting morels is labor-intensive, as they need to be foraged by hand. Their short growing season, high dependence on weather conditions, and demand in gourmet cuisine also contribute to their high price.
Can I eat Morchella?
Yes, Morchella mushrooms are edible and highly sought after for their unique flavor and texture. However, it is essential to correctly identify them to avoid potential toxic look-alikes. Always ensure that you are consuming true morel mushrooms, as confirmed by an expert or reliable guide.
What is the scientific name of Morchella?
The scientific name for morel mushrooms is Morchella. It is a genus comprising numerous species found worldwide, such as Morchella esculenta, Morchella americana, and Morchella tomentosa, among others.
How do you pronounce Morchella?
Morchella is pronounced as mor-KELL-uh.
What are the benefits of Morchella esculenta?
Morchella esculenta, commonly known as the yellow morel or common morel, is renowned for its unique taste and culinary applications. It is a good source of vitamin D and is rich in antioxidants, which can offer potential health benefits. Some studies suggest that Morchella esculenta may have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties as well. However, they should always be cooked before consumption, as raw morels can cause gastrointestinal distress.


